Our Energy Portfolio
Each year, BED sources the energy required to cover its total “load,” which is the total of annual retail sales to customers, company use (electricity used by BED’s own facilities and electric fleet vehicles), and the line losses incurred on the distribution and transmission systems (which are approximately 3% of annual sales). Many generating resources are inherently variable, so the amount of production in any year will fluctuate. For CY2024, BED’s renewable resources provided over 100% of both BED retail sales and load.
The table below shows the resources that provided BED’s energy supply in 2024.
BED Energy Supply, January-December 2024
| Winter Peak MW | 47.8 | |||
| Summer Peak MW | 61.6 | |||
| Energy Use (MWh) | 330,068 | |||
| Resource | Fuel Type | Location | Capacity (MW) | Energy (MWH) |
| McNeil | Wood | Vermont | 25.0 | 98,522 |
| Hancock | Wind | Maine | 13.5 | 31,038 |
| Sheffield | Wind | Vermont | 16.0 | 28,103 |
| Georgia Mountain Community | Wind | Vermont | 10.0 | 26,970 |
| Hydro-Québec | Large Hydro | Quebec | n/a | 52,704 |
| NYPA | Large Hydro | New York | 2.6 | 17,708 |
| Winooski One | Small Hydro | Vermont | 7.4 | 29,517 |
| Great River Hydro | Small Hydro | Vermont | n/a | 43,920 |
| Burlington | Solar | Vermont | 3.4 | 5,069 |
| BED Gas Turbine | Oil | Vermont | 22.0 | 358 |
| First Light | Hydro | Connecticut | n/a | 5,254 |
| ISO New England Exchange – Net Sales | Various (system mix) | New England | n/a | -8,327 |
| Total Gross Generation & Purchases | 333,164 |
BED Fuel Types and Renewability
2024 Sources Prior to Renewable Attribute REC Sales and Purchases
CY 2024 BED Fuel Types Prior to REC Transactions
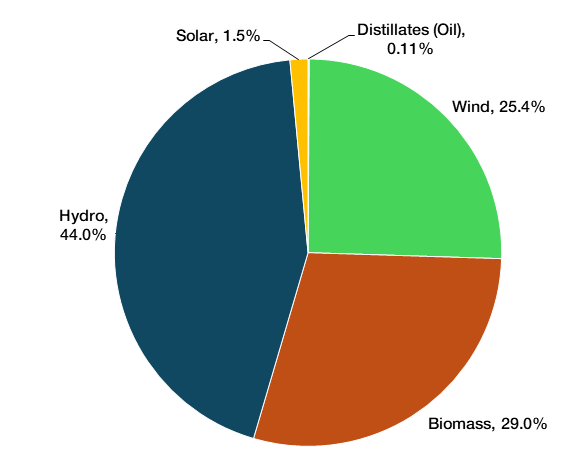
NOTE: BED has no contracts for resources fueled by Natural Gas, Nuclear or Coal. 0.1% of generated energy comes from Oil used at the BED Gas Turbine. The above represents energy generated and purchased by BED prior to REC sales and amounts to 339,164 MWh of electricity. The chart does not represent an ability to claim those fuel types for renewability.
After Accounting for Renewable Attribute REC Sales and Purchases
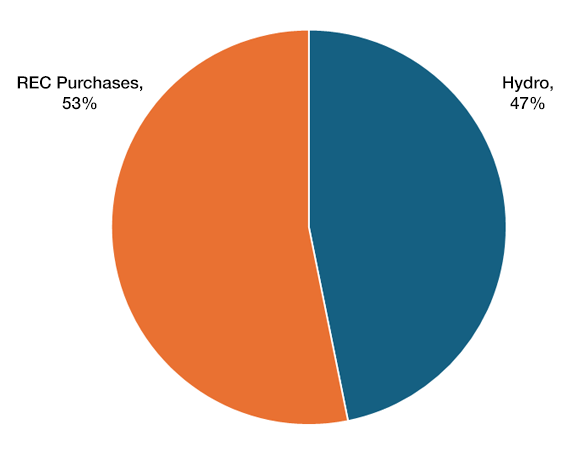
In order to verify that its energy portfolio is 100% renewable under Vermont’s Renewable Energy Standard (RES), each year BED must retire a certain number of Renewable Energy Credits (RECs). BED receives RECs for each MWh of renewable energy that BED generates or purchases under its contracts. Sales of RECs are allowed under BED’s integrated resource plan and help BED control the rate impacts of purchasing newer renewable resources (which are generally more expensive than older renewable resources or non-renewable alternatives). BED sells some of its higher-value RECs from its owned or contracted sources and purchases lower-cost RECs from the renewable resource market for RES compliance purposes, and to maintain an energy portfolio that is 100 percent renewably sourced.
In CY2024 BED sold RECs representing approximately 228,000 MWh of generation and received revenues of approximately $7.4 million – approximately 12% of its cost of service. BED retired Vermont-qualified RECs to replace any RECs sold that it would have needed to comply with Vermont’s RES in 2024. In 2024, BED was required to retire RECs from generators qualified by the State of Vermont equivalent to BED’s annual retail sales. However, for 2024 BED voluntarily reserved/retired RECs equivalent to BED’s 2024 load, or 330,068 RECs, in excess of its 2024 sales of 322,588 MWh. All RECs retired in 2024 were from hydroelectric resources. (In 2025, the Vermont RES will require all utilities to retire RECs based on their load.)
2024 BED Renewability After REC Transactions
The following table represents the emission profile of the RECs that BED retired for 2024 as tracked by the New England Power Pool Generator Information System (note “-“ represents a zero value as for 2024 all RECs retired were from hydroelectric resources).
| Carbon Dioxide | Carbon Monoxide | Mercury | Nitrogen Oxide | Organic Compounds | Particulates | Particulates (<10 microns) | Sulphur Dioxides | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewability lbs. per MWh |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
